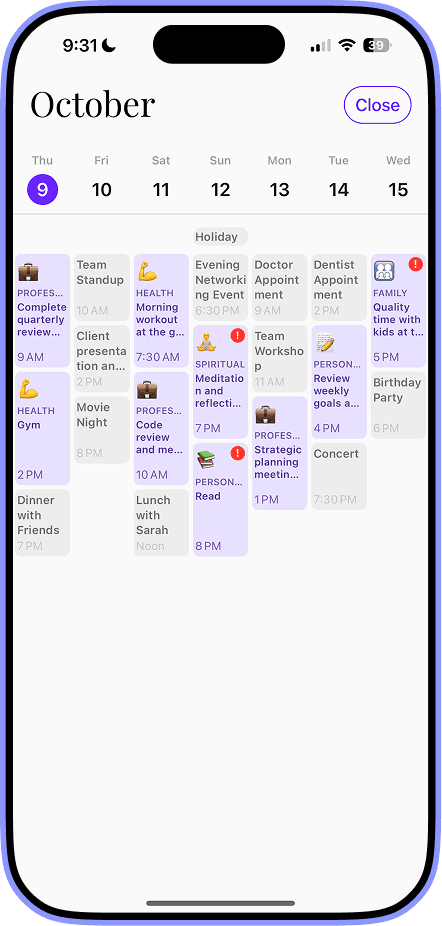
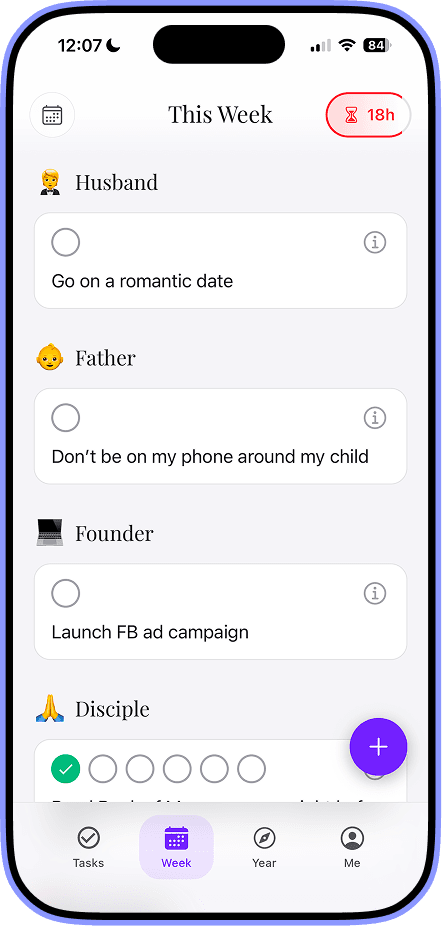
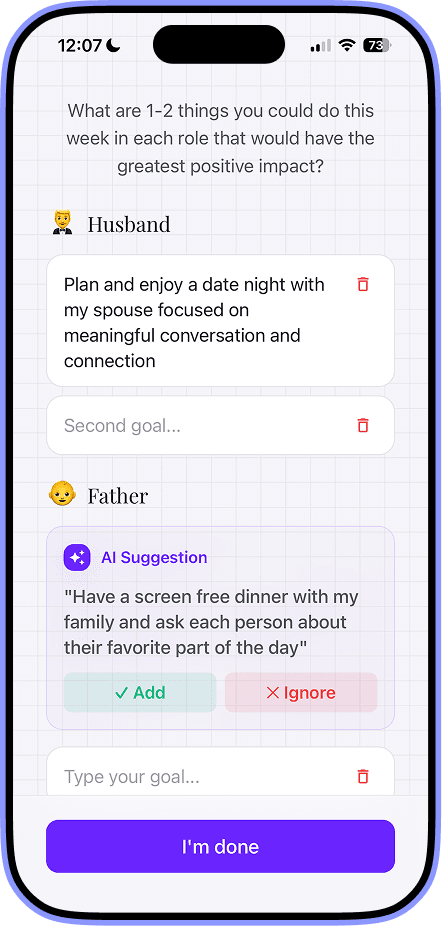
Examples of Operational Planning: 7 Real-World Insights
Discover examples of operational planning in 7 real-world scenarios from production to project management and gain practical strategies to optimize ops.

Strategic goals often feel distant and abstract, but operational planning is where vision becomes reality. This is the practical, day-to-day process that defines the 'who, what, when, and how' required to achieve your high-level objectives. It’s the essential bridge between ambition and tangible results, ensuring that daily actions directly contribute to long-term success. Without a solid operational plan, even the best strategies remain just ideas.
This guide moves past theory to provide concrete, actionable insights. We will dissect seven powerful examples of operational planning across different business functions, from production scheduling to financial allocation and project management. For each example, we'll break down its strategic purpose, tactical execution, and key takeaways you can immediately apply.
You'll discover replicable methods to streamline your own processes, whether you're managing a factory floor, a software project, or a service team. To keep these complex plans aligned and easily accessible, tools like Harmony AI can centralize your operational workflows, ensuring every team member is synchronized and focused on the right tasks. Let's explore how to transform your strategic objectives into operational excellence.
1. Production Planning and Scheduling
Production planning and scheduling is a quintessential example of operational planning that directly translates high-level strategic goals into tangible, day-to-day manufacturing activities. It is the process of coordinating all necessary resources, including labor, materials, and machinery, to produce specific goods within a set timeframe. This plan dictates what will be made, how much will be made, and when it will be made to meet customer demand efficiently and cost-effectively.
At its core, this type of planning ensures that production flows smoothly, minimizing waste and maximizing output. It is the operational backbone for companies like Toyota, whose groundbreaking Just-In-Time (JIT) system ensures parts arrive precisely when needed, slashing inventory costs. Similarly, complex operations like Boeing's aircraft assembly rely on meticulous production scheduling to manage thousands of components and intricate assembly stages.
Strategic Breakdown
The power of production planning lies in its ability to optimize resource allocation and align daily tasks with broader business objectives, such as profitability and market share. It is a dynamic process that must adapt to real-time changes in demand, supply chain disruptions, and equipment performance.
Key Insight: Effective production planning is not a static document but a continuous feedback loop. It relies on constant communication between sales (demand forecasting), procurement (material availability), and the production floor (capacity and execution).
Actionable Takeaways for Implementation
To integrate this operational planning example into your own processes, focus on creating a clear, data-driven framework.
- Start with Demand Forecasting: Use historical sales data and market analysis to create an accurate forecast. This is the foundation of your entire production plan.
- Use the Right Tools: Leverage production planning software or MRP (Material Requirements Planning) systems to automate scheduling, track inventory, and manage resources. For coordinating cross-departmental communication and task dependencies, a tool like the Harmony AI app can ensure teams from sales to procurement stay perfectly aligned.
- Build in Flexibility: Incorporate buffer time into your schedules to account for unforeseen issues like machine maintenance or supplier delays.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly review key performance indicators (KPIs) like production output, cycle time, and on-time delivery. Use this data to refine and adjust your operational plan continuously.
2. Workforce Scheduling and Labor Planning
Workforce scheduling and labor planning is a crucial example of operational planning focused on assigning employees to specific shifts and tasks. It is the process of balancing business needs, such as customer demand and production targets, with employee availability, skills, and labor regulations. This plan ensures optimal staffing levels are maintained to guarantee service quality and operational efficiency without overspending on labor costs.
This type of planning is the lifeblood of service-oriented and labor-intensive industries. For example, Starbucks utilizes a sophisticated system that analyzes customer traffic patterns to adjust barista schedules, ensuring stores are well-staffed during peak hours. Similarly, hospitals rely on meticulous nurse scheduling to provide continuous, high-quality patient care, while Amazon's fulfillment centers use advanced labor planning to manage massive warehouse teams and meet tight delivery deadlines.
Strategic Breakdown
Effective workforce scheduling directly connects daily staffing decisions to broader strategic goals like customer satisfaction, employee retention, and profitability. It is a highly dynamic process that must account for seasonality, unexpected employee absences, and fluctuating consumer demand, making it a cornerstone of agile business operations.
Key Insight: Great workforce planning goes beyond just filling shifts; it treats labor as a strategic asset. It involves forecasting needs, developing employee skills, and creating flexible schedules that boost morale and productivity.
Actionable Takeaways for Implementation
To implement a robust workforce scheduling process, focus on creating a system that is both data-informed and employee-centric.
- Analyze Historical Data: Use past sales, customer traffic, or production data to accurately forecast your staffing needs for upcoming weeks and months.
- Leverage Workforce Management Software: Utilize tools like UKG or Deputy to automate scheduling, track time, and manage compliance. For seamless communication and task handoffs between scheduled shifts, a platform like the Harmony AI app can centralize instructions and ensure continuity.
- Promote Flexibility and Communication: Publish schedules well in advance and implement a clear, fair system for employees to request time off or swap shifts.
- Cross-Train Your Team: Develop a multi-skilled workforce to provide greater scheduling flexibility and cover for unexpected absences without disrupting operations. You can learn more about optimizing these handoffs with digital workflow automation.
3. Inventory Management and Stock Control
Inventory management and stock control is another critical example of operational planning focused on balancing supply and demand. It involves creating and executing a detailed plan to determine optimal stock levels, set reorder points, and schedule replenishment to ensure product availability while minimizing carrying costs like storage, insurance, and obsolescence. This plan governs the day-to-day tracking of inventory, demand forecasting, and warehouse management.
At its heart, this type of planning prevents both stockouts, which lead to lost sales, and overstocking, which ties up capital. It is the operational lifeblood for giants like Walmart, whose sophisticated, data-driven system tracks products from supplier to shelf in real-time. Similarly, Amazon's predictive inventory placement model uses operational planning to position goods in fulfillment centers closest to anticipated customer demand, drastically reducing shipping times.
Strategic Breakdown
The strategic value of inventory management lies in its direct impact on cash flow, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency. A well-executed inventory plan transforms a static warehouse into a dynamic, responsive asset that supports strategic goals such as market responsiveness and profitability. It requires a delicate balance, constantly adapting to sales velocity and supply chain realities.
Key Insight: Superior inventory control is not just about counting stock; it's about making data-informed predictions. It relies on a tight integration between sales forecasts, procurement schedules, and real-time logistics data to create a fluid and cost-effective supply chain.
Actionable Takeaways for Implementation
To implement a robust inventory management plan, focus on creating a system that is both precise and agile.
- Segment Your Inventory: Use ABC analysis to classify items based on their value (A-items being most valuable, C-items least). This helps you prioritize management efforts on the products that matter most.
- Leverage Technology: Employ inventory management software like NetSuite or Fishbowl to automate tracking, reordering, and reporting. To ensure your purchasing and sales teams are on the same page for demand planning, a tool like the Harmony AI app can centralize communication and track related tasks seamlessly.
- Establish Key Metrics: Define and regularly monitor KPIs such as inventory turnover rate, carrying costs, and stock-to-sales ratio.
- Build Supplier Relationships: Work closely with reliable suppliers to shorten lead times and explore strategies like Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory, which reduces the need to hold large amounts of stock.
4. Budget and Financial Resource Allocation
Budgeting and financial resource allocation is a critical example of operational planning that translates strategic ambitions into a quantifiable financial roadmap. This process involves assigning monetary resources to various departments, projects, and activities for a specific period, such as a quarter or a fiscal year. It ensures that every dollar spent is deliberate, controlled, and aligned with overarching business objectives.
This type of planning is the lifeblood of an organization, dictating the scope and scale of all other operational activities. It prevents overspending, ensures financial stability, and directs capital toward high-priority initiatives. A well-known model is Google's 70/20/10 rule, which allocates 70% of resources to the core business, 20% to emerging projects, and 10% to experimental ventures. Similarly, municipal governments use this planning to allocate taxpayer money to essential services like public safety and infrastructure.
Strategic Breakdown
Effective financial planning moves beyond simple expense tracking; it becomes a strategic tool for prioritizing goals and driving performance. It forces departments to justify their resource needs in the context of company-wide targets, fostering a culture of accountability and efficiency. The plan must be agile enough to adapt to market shifts, unexpected costs, or new opportunities.
Key Insight: A budget is not just a restrictive document; it is an active management tool. It provides the framework for making informed trade-offs and measuring the financial impact of every operational decision.
Actionable Takeaways for Implementation
To implement robust financial operational planning, focus on creating a transparent, collaborative, and data-driven process.
- Involve Department Heads: Engage managers in the budgeting process. Their frontline knowledge ensures projections are realistic and fosters a sense of ownership over financial performance.
- Link Budget to Objectives: Each line item in the budget should directly support a specific strategic goal. This clarifies spending priorities and makes it easier to allocate funds effectively, a core component of robust priority management systems.
- Build in Contingency: Allocate a contingency reserve (typically 5-10% of the total budget) to handle unforeseen expenses or opportunities without derailing the entire plan.
- Use the Right Tools: Utilize budgeting software to automate tracking and reporting. For ensuring all teams understand how their budgets connect to larger project timelines and deliverables, a tool like the Harmony AI app can provide crucial visibility and alignment across the organization.
- Review and Adapt Regularly: Don't wait for the annual review. Conduct quarterly or even monthly budget reviews to compare actual spending against the plan and make necessary adjustments.
5. Supply Chain and Logistics Coordination
Supply chain and logistics coordination is a critical example of operational planning focused on the end-to-end movement of goods, services, and information. It orchestrates every step from raw material sourcing and supplier management to manufacturing, warehousing, and final delivery to the customer. This planning ensures products are in the right place, at the right time, and in the most cost-effective manner.
This operational discipline is the lifeblood of global commerce. For instance, FedEx’s legendary hub-and-spoke model revolutionized overnight delivery through meticulous logistics planning. Similarly, McDonald's coordinates a vast global network to deliver standardized ingredients to over 40,000 restaurants daily, ensuring consistency and quality control on a massive scale.
Strategic Breakdown
Effective supply chain planning directly impacts a company's bottom line by minimizing costs, improving customer satisfaction, and building resilience against disruptions. It translates strategic goals like market responsiveness and cost leadership into daily operational realities, such as warehouse staffing, transportation scheduling, and inventory levels.
Key Insight: A modern supply chain is not just a cost center; it is a strategic asset. Operational planning must move beyond simple logistics to create an agile, transparent, and collaborative network that can adapt to rapid changes in market demand and global events.
Actionable Takeaways for Implementation
To improve supply chain and logistics coordination, focus on visibility, collaboration, and proactive risk management.
- Map Your Entire Supply Chain: Gain full visibility by mapping every supplier, transportation link, and warehouse. Understanding the complete flow is the first step to identifying risks and inefficiencies.
- Implement Robust Tracking Systems: Use technology like RFID, GPS, and supply chain management (SCM) software to enable real-time tracking and tracing of goods from origin to destination.
- Foster Supplier Collaboration: Treat suppliers as partners. Share demand forecasts and production plans to improve their planning accuracy. A collaborative platform like the Harmony AI app can centralize this communication, ensuring suppliers and internal teams are always in sync on timelines and requirements.
- Conduct Regular Risk Assessments: Proactively identify potential disruptions, such as geopolitical instability, natural disasters, or single-source supplier dependencies, and develop contingency plans.
6. Project Execution and Task Management
Project execution and task management serve as a critical example of operational planning, transforming high-level strategic projects into a structured series of day-to-day actions. This process involves creating detailed work breakdown structures, assigning tasks, defining timelines, and allocating resources to ensure complex initiatives are completed on schedule and within budget. It is the engine that drives projects from conception to completion.
This type of planning is indispensable across industries. For example, NASA’s multi-year Mars Rover missions rely on it to coordinate thousands of tasks across scientific and engineering teams. Similarly, construction firms use the Critical Path Method (CPM) for massive infrastructure projects, while software companies leverage Agile sprints to manage development cycles and deliver new features incrementally.
Strategic Breakdown
Effective project execution planning provides clarity and accountability, ensuring every team member understands their role and how their tasks contribute to the project's overall success. It mitigates risks by identifying potential bottlenecks and dependencies early, allowing managers to adapt proactively rather than reactively. This detailed operational foresight is a cornerstone of business process optimization and is essential for achieving strategic goals.
Key Insight: The success of a project is determined not just by the grand vision but by the daily management of its smallest components. Meticulous task management is the bridge between strategy and successful execution.
Actionable Takeaways for Implementation
To apply this operational planning example to your own initiatives, focus on creating a transparent and disciplined management system.
- Define Clear Success Criteria: Before work begins, establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for the project.
- Utilize Project Management Tools: Employ software like Asana, Monday.com, or Microsoft Project to visualize timelines, track progress, and manage tasks. For integrating these efforts with your broader communication and goal-setting, the Harmony AI app helps keep all project stakeholders aligned and informed.
- Hold Daily Stand-up Meetings: Implement brief, daily check-ins to discuss progress, identify immediate obstacles, and keep the team synchronized.
- Conduct Post-Project Reviews: After a project concludes, hold a retrospective meeting to analyze what went well and what could be improved, capturing valuable lessons for future operational planning.
7. Quality Control and Compliance Planning
Quality control and compliance planning is a critical example of operational planning focused on establishing the daily procedures and standards that ensure products or services consistently meet predetermined requirements. This involves setting up specific checkpoints, testing protocols, and documentation processes to maintain quality and adhere to industry regulations. It's the operational framework that translates high-level goals like "customer satisfaction" and "brand reputation" into measurable, day-to-day actions.
This type of planning is the bedrock of highly regulated industries. For instance, pharmaceutical companies use it to ensure every batch of medication meets strict FDA standards, while automotive manufacturers like those adhering to IATF 16949 standards rely on it to produce safe and reliable vehicles. Similarly, Motorola's pioneering use of Six Sigma transformed quality management from a reactive "fix-it" process into a proactive, data-driven strategy to minimize defects.
Strategic Breakdown
The strategic value of quality control planning lies in its ability to mitigate risk, reduce waste, and build long-term customer trust. By embedding quality checks directly into workflows, companies can identify and correct issues early, preventing costly recalls or reputational damage. It transforms quality from an afterthought into an integral part of the operational process, directly supporting business objectives like profitability and market leadership.
Key Insight: Proactive quality planning is a competitive advantage. It shifts the focus from simply catching errors to designing processes where errors are less likely to occur, fostering a culture of continuous improvement pioneered by figures like W. Edwards Deming.
Actionable Takeaways for Implementation
To effectively integrate quality control planning into your operations, focus on creating a documented and systematic approach that involves the entire team.
- Define Clear Quality Metrics: Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) quality standards. What does "high quality" actually mean for your product or service?
- Document Everything: Create detailed standard operating procedures (SOPs) and maintain meticulous records for every inspection, test, and corrective action. This creates an essential audit trail for compliance.
- Empower Your Entire Team: Train all employees on quality standards, not just the QC department. When everyone understands their role in maintaining quality, the entire system becomes more robust. The Harmony AI app can be used to assign and track training tasks, ensuring all team members are up-to-date on compliance protocols.
- Conduct Regular Internal Audits: Don't wait for an external audit to find problems. Perform regular internal checks to identify and address non-compliance issues proactively, using the findings to refine your operational plan.
7-Point Operational Planning Comparison
| Area | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes ⭐📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages |
| Production Planning and Scheduling | High 🔄 — multi-source data, MRP, real-time adjustment | High ⚡ — ERP/MRP software, planners, integration | High ⭐⭐ — improved efficiency, on-time delivery, lower waste 📊 | Discrete/manufacturing lines, multi-component assembly | Optimizes capacity & inventory, improves quality consistency |
| Workforce Scheduling and Labor Planning | Medium 🔄 — shift rules, compliance, preferences | Medium ⚡ — WFM software, HR coordination | Medium ⭐ — better coverage, lower overtime, higher satisfaction 📊 | Retail, healthcare, call centers, 24/7 operations | Ensures staffing coverage, reduces labor cost, boosts morale |
| Inventory Management and Stock Control | Medium 🔄 — forecasting, SKU complexity | Medium–High ⚡ — IMS/WMS, data analytics, supplier coordination | High ⭐⭐ — fewer stockouts, lower carrying costs, improved turnover 📊 | Retail, e-commerce, distribution, manufacturing | Balances availability vs. cost, improves cash flow, reduces obsolescence |
| Budget and Financial Resource Allocation | Medium 🔄 — forecasting, cross-functional alignment | Low–Medium ⚡ — finance tools, analysts, stakeholder input | Medium ⭐ — financial control, aligned spending, variance visibility 📊 | Enterprises, departments, project portfolios, public sector | Aligns spending to strategy, enables cost control and decision making |
| Supply Chain and Logistics Coordination | Very High 🔄 — network optimization, external partners | High ⚡ — SCM systems, transport, warehouse, supplier networks | High ⭐⭐ — lower logistics cost, faster fulfillment, greater visibility 📊 | Global distribution, multi-facility operations, retail chains | Reduces lead times/costs, increases resilience and end-to-end visibility |
| Project Execution and Task Management | Medium 🔄 — dependencies, resource leveling | Medium ⚡ — PM tools, cross-functional teams | Medium–High ⭐ — timely delivery, accountability, risk mitigation 📊 | New product launches, construction, IT/implementation projects | Improves delivery predictability, clarifies ownership, optimizes resources |
| Quality Control and Compliance Planning | Medium–High 🔄 — SOPs, audits, documentation | Medium ⚡ — QC tools, testing, training, documentation | High ⭐⭐ — fewer defects, regulatory compliance, brand protection 📊 | Pharma, food, healthcare, regulated manufacturing | Ensures compliance, reduces recalls/rework, enhances process consistency |
From Operational Plans to Personal Purpose
Throughout this article, we've explored a diverse range of examples of operational planning, from the factory floor's production schedules to the meticulous details of a project's task management system. We've seen how organizations translate high-level strategic goals into the tangible, daily actions that drive results. The common thread connecting every successful example, whether in inventory management or workforce scheduling, is the principle of intentional execution. It’s about transforming ambiguity into a clear, actionable roadmap.
This principle doesn't just apply to large-scale business operations; it holds the key to personal and professional fulfillment. Think of your life's ambitions as your strategic goals. Without a clear operational plan to guide your daily efforts, even the most inspiring vision can remain a distant dream. The same structured approach that ensures a supply chain runs smoothly can bring order and progress to your own multifaceted life.
Key Takeaways: From Corporate Strategy to Personal Systems
The core lesson from these operational planning examples is that success is built on a foundation of consistent, well-organized actions. Here are the most critical takeaways you can adapt for your own growth:
- Break Down Your 'Why': Just as a business's mission informs its operational plan, your personal purpose should guide your daily tasks. Connect what you do every day to who you want to become.
- Allocate Your Resources Wisely: Your most valuable resources are your time, energy, and focus. Like a financial budget, you must allocate these intentionally across your key life roles, such as your career, family, health, and personal development.
- Monitor and Adapt: Effective operational plans are not static. They involve regular check-ins and adjustments. Similarly, a weekly review of your personal progress allows you to adapt to new challenges and opportunities, ensuring you stay on track.
Your Next Step: Building Your Personal Operational Plan
Mastering operational planning within an organization is a powerful skill. Applying it to your own life is transformative. It's the bridge between setting goals and actually achieving them, turning your strategic vision for your life into a daily reality. This is where you move from passively hoping for a better future to actively building it, one well-planned day at a time. The structure and clarity that guide a successful project are the same tools that can help you live a more purposeful and accomplished life.
This is the philosophy behind Harmony AI. It’s designed to help you define your Personal Mission Statement, your ultimate 'why', and then systematically translate it into a balanced weekly plan. By organizing your goals and tasks around your most important roles ('Team Lead,' 'Parent,' 'Lifelong Learner'), Harmony ensures that your daily actions are always aligned with your core purpose. The app's intelligent scheduling and gentle check-ins provide the structure needed to bridge the gap between intention and consistent action, acting as your personal operational manager. If you're ready to apply the proven power of structured planning to your own life, it’s time to build your own system for success.
Ready to turn your personal and professional ambitions into an actionable plan? Discover how Harmony AI can help you align your daily tasks with your life's mission, creating the structure you need to achieve your biggest goals. Download Harmony AI today and start living your purpose, intentionally.
Harmony - AI Planner
Plan your weeks, plan your life. Define your mission, plan weeks around your roles, and stay on track every day with AI guidance.
Download FreePersonal Mission
Define your deeper why
Weekly Planning
Role-based goal setting
AI Guidance
Smart suggestions & nudges
Celebrations
Stay motivated daily